Automate CloudWatch Agent Setup on EC2 Using User Data Scripts
Let's automate CloudWatch Agent installation on EC2 instances using User Data scripts. New instances in your Auto Scaling Group will automatically send custom metrics without manual configuration.
Every time an instance is added to your Auto Scaling Group, you need to manually install and configure the CloudWatch Agent.
This doesn't scale well and is error-prone.
User Data scripts solve this problem by running commands automatically when an EC2 instance boots up.
In this post, we'll walk through:
- What User Data scripts are and when to use them
- Automating CloudWatch Agent installation with User Data
- Configuring the agent in your AWS CDK code
This video is part of my Amazon EC2 series and thanks to AWS for sponsoring it.
This post assumes you're familiar with basic CloudWatch Agent setup. If you're new to CloudWatch Agent, check out the manual setup guide first.
The Problem with Manual CloudWatch Agent Setup
In the previous post, we manually configured the CloudWatch Agent on EC2 instances to collect memory, disk, and process metrics.
Setting Up CloudWatch Agent on EC2: Monitor Memory and Disk Usage

This works fine for a few instances, but what happens when your Auto Scaling Group scales out and adds new instances?, an instance is replaced due to health checks? or when you need to recreate your infrastructure?
You'd have to manually configure CloudWatch Agent on every new instance. Not ideal.
What is User Data in Amazon EC2?
User Data is a script that runs automatically when an EC2 instance first boots up.
You can use it to install packages and software, configure applications, set up monitoring agents, run initialization scripts etc.
This makes User Data perfect for automating CloudWatch Agent installation.
User Data scripts run with root privileges and execute before the instance is fully available. Keep your scripts fast and focused on essential initialization tasks.
Setting Up EC2 User Data Scripts in AWS CDK
Let's update our CDK code to include a User Data script that installs and configures the CloudWatch Agent automatically.
If you've been following along with this series, you already have a CDK project that sets up an Auto Scaling Group with EC2 instances.
Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling Groups with .NET and AWS CDK

Before we add the User Data script, ensure your EC2 instance role has the required IAM policies. We added these in the previous post where we manually set up the CloudWatch agent.
role.AddManagedPolicy(ManagedPolicy.FromAwsManagedPolicyName("AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore"));role.AddManagedPolicy(ManagedPolicy.FromAwsManagedPolicyName("AmazonEC2ReadOnlyAccess"));role.AddManagedPolicy(ManagedPolicy.FromAwsManagedPolicyName("CloudWatchAgentServerPolicy"));
These policies allow the CloudWatch Agent to be installed via Systems Manager, read EC2 metadata, send metrics to CloudWatch.
The CloudWatch Agent Configuration
First, let's define the CloudWatch Agent configuration as a JSON object in our CDK code:
var cloudWatchConfig = new{agent = new{metrics_collection_interval = 60},metrics = new{@namespace = "CWAgent",metrics_collected = new{mem = new{measurement = new[]{new { name = "mem_used_percent", rename = "MemoryUsedPercent", unit = "Percent" },new { name = "mem_available_percent", rename = "MemoryAvailablePercent", unit = "Percent" }}},cpu = new{measurement = new[]{new { name = "cpu_usage_active", rename = "CPUUsageActive", unit = "Percent" }}},disk = new{measurement = new[]{new { name = "disk_used_percent", rename = "DiskUsedPercent", unit = "Percent" },new { name = "disk_free", rename = "DiskFree", unit = "Gigabytes" }}},processes = new{measurement = new[]{new { name = "running", rename = "ProcessesRunning", unit = "Count" }}}}}};var configJson = JsonSerializer.Serialize(cloudWatchConfig);
This configuration specifies collection interval of 60 seconds, custom namespace "CWAgent" for organizing metrics, and some example metrics - memory, CPU, disk, and process metrics to collect
You can customize this configuration based on your needs. Use the AWS Console wizard to generate the JSON if you're unsure which metrics to collect.
Creating the User Data Script
Now let's create the User Data script that installs and configures the CloudWatch Agent:
var userData = UserData.ForLinux();userData.AddCommands("yum update -y");// Install CloudWatch AgentuserData.AddCommands("yum install -y amazon-cloudwatch-agent");userData.AddCommands("mkdir -p /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/etc/");// Write the CloudWatch Agent configurationuserData.AddCommands($@"cat > /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/etc/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.json << 'EOF'{configJson}EOF");// Verify the config file was createduserData.AddCommands("ls -la /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/etc/");userData.AddCommands("cat /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/etc/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.json");// Start the CloudWatch Agent with the configurationuserData.AddCommands("/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/amazon-cloudwatch-agent-ctl " +"-a fetch-config " +"-m ec2 " +"-s " +"-c file:/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/etc/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.json");// Enable and start the serviceuserData.AddCommands("systemctl enable amazon-cloudwatch-agent");userData.AddCommands("systemctl start amazon-cloudwatch-agent");userData.AddCommands("systemctl status amazon-cloudwatch-agent");
The script updates yum, installs the CloudWatch Agent, configures it with our JSON settings, verifies the setup, and starts the service with auto-boot enabled.
Finally, attach the User Data script to your Launch Template.
var launchTemplate = new LaunchTemplate(this, "WebApiLaunchTemplate", new LaunchTemplateProps{InstanceType = InstanceType.Of(InstanceClass.BURSTABLE3, InstanceSize.MICRO),MachineImage = MachineImage.LatestAmazonLinux2023(),Role = role,SecurityGroup = securityGroup,UserData = userData, // Attach the User Data scriptKeyPair = KeyPair.FromKeyPairName(this, "KeyPair", "my-key-pair")});
The Launch Template is used by your Auto Scaling Group to create new instances, so every new instance will run this User Data script.
With the User Data script in place, let's deploy the updated CDK stack using cdk deploy
This creates a new Launch Template version with User Data, but existing instances won't be recycled automatically. New instances will use the updated version, while old instances remain on version 1.
To test the automation, terminate an existing instance (EC2 → Auto Scaling Groups → Instance management → select instance → Actions → Terminate instance) and watch the Auto Scaling Group create a replacement with the new configuration.
The Auto Scaling Group will detect the missing instance and automatically create a replacement using the new Launch Template version.
Viewing the User Data Script Logs
Once the new instance is running, you can verify the User Data script executed successfully.
Navigate to the new instance:
- Select the instance with Launch Template version 2
- Go to Actions → Monitor and troubleshoot → Get system log
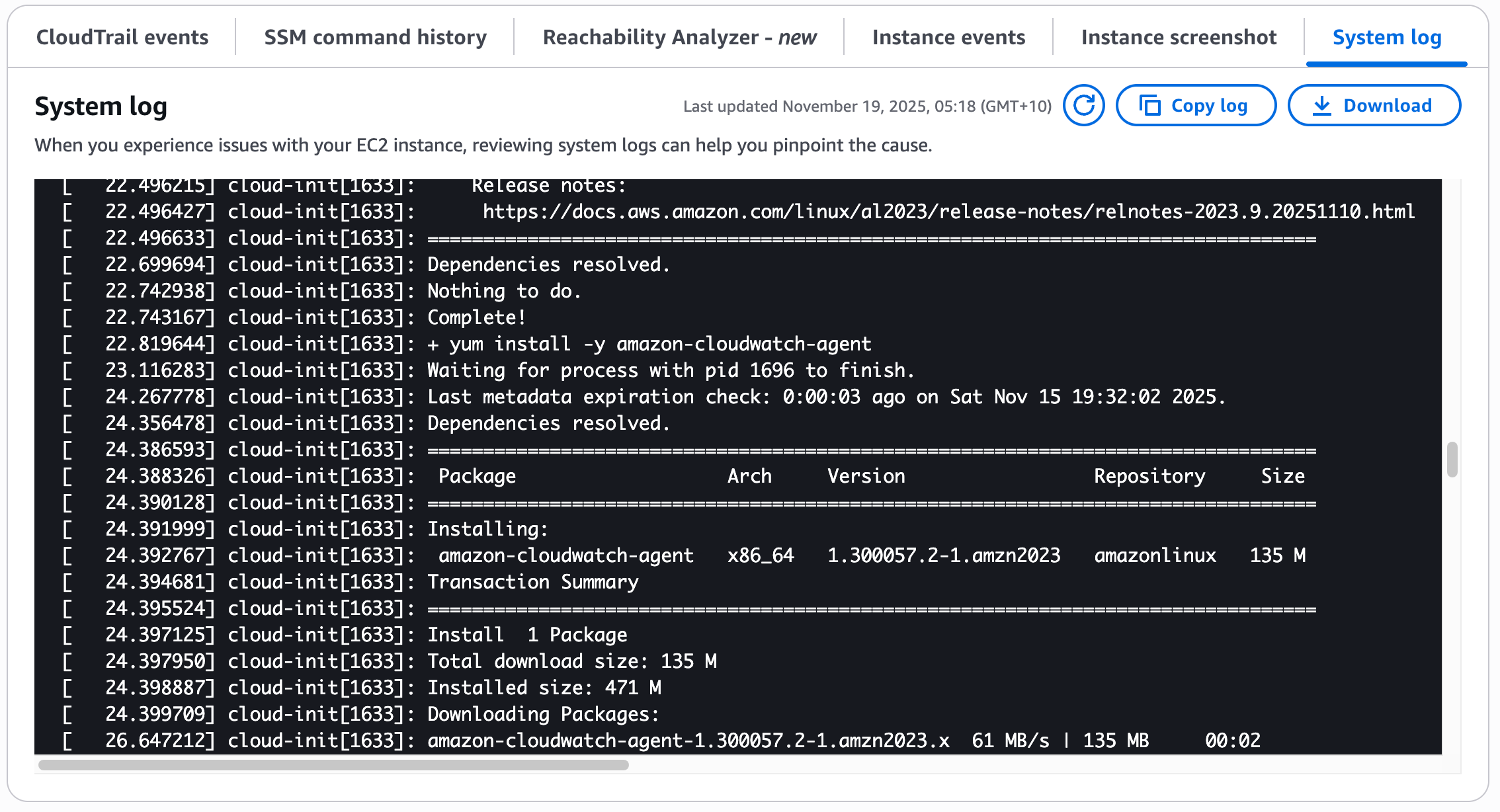
In the system log, you'll see:
yum updateandyum installcommands executing- CloudWatch Agent configuration file being created
- The agent starting up successfully
systemdservice being enabled
This confirms the User Data script ran successfully during instance initialization.
Verifying CloudWatch Metrics
After about 60 seconds (based on our collection interval), metrics should start appearing in CloudWatch.
Navigate to your EC2 instance and go to the Monitoring tab. Make sure to enable Include metrics in the CW agent namespace to see the custom metrics.
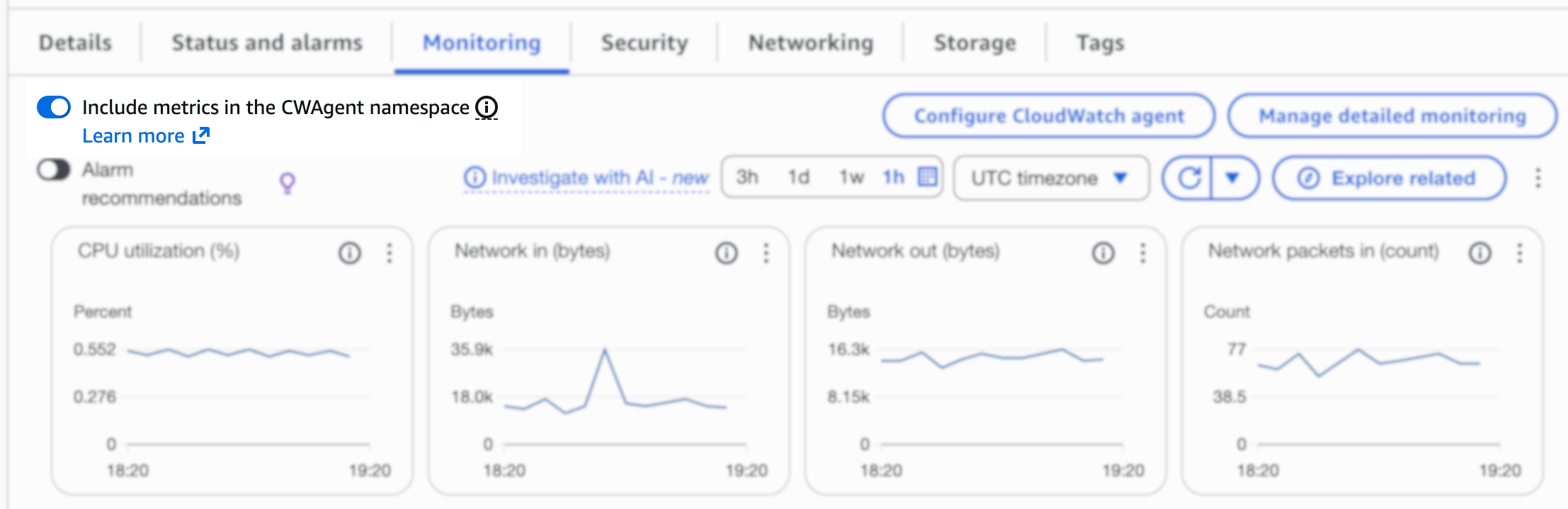
You should see:
- Disk used percentage
- Disk free space
- Memory used percentage
- Memory available percentage
- Process count
All without any manual configuration!
Testing with Multiple Instances
Let's test further by:
- Terminating another old instance (version 1)
- Increasing the desired capacity to add a new instance
Update your Auto Scaling Group's desired capacity from 2 to 3. The Auto Scaling Group will:
- Terminate the version 1 instance and replace it with version 2
- Add a new instance (version 2) to reach the desired capacity of 3
All new instances will automatically have CloudWatch Agent configured and sending metrics.
Viewing the User Data Script
You can view the User Data script attached to any instance:
- Navigate to the instance details
- Go to Actions → Instance settings → Edit user data
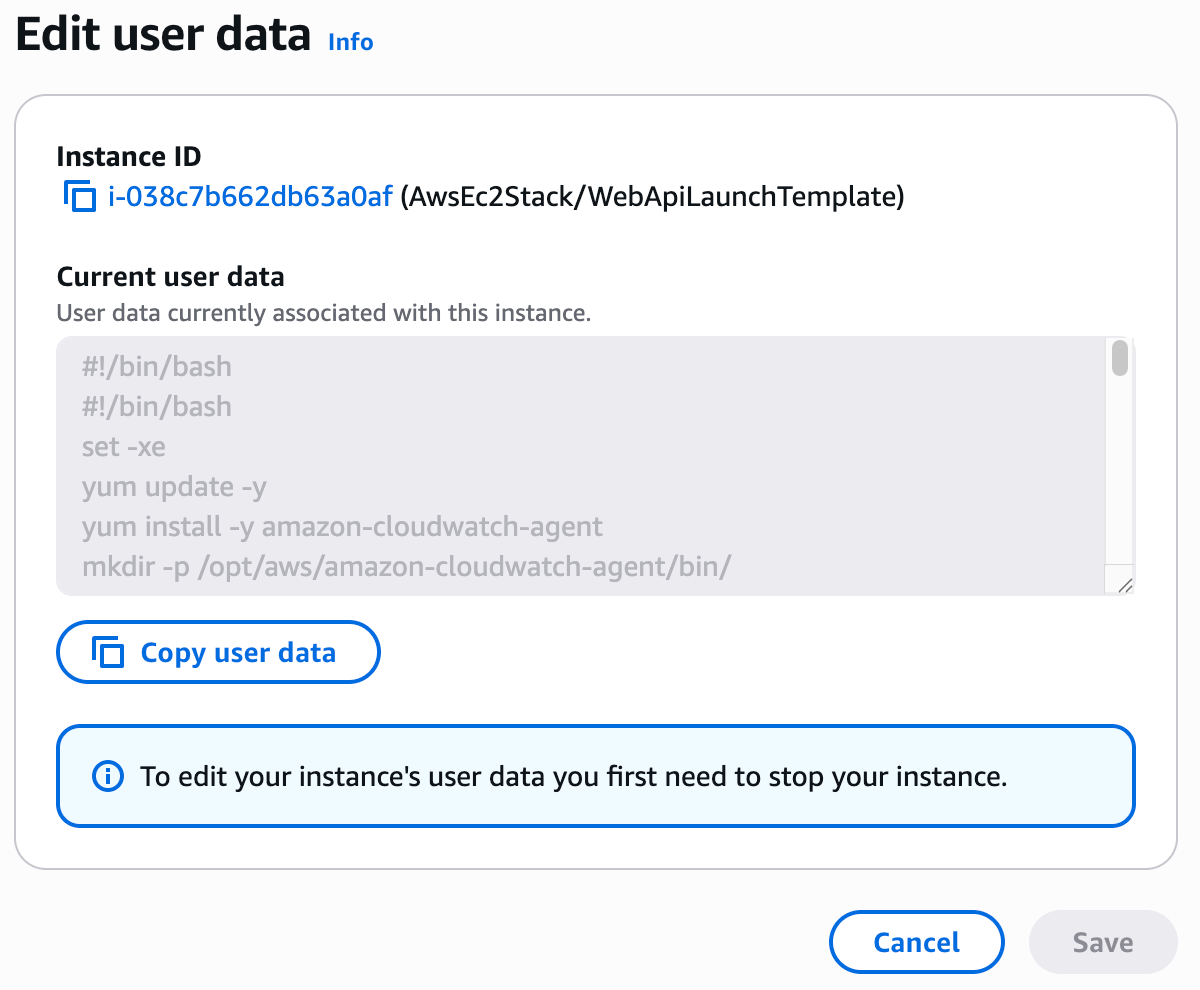
User Data is stored as plain text. Never include sensitive information like passwords, API keys, or credentials in User Data scripts. Use AWS Secrets Manager or Parameter Store instead.
Generating CloudWatch Agent Configuration
If you're unsure what metrics to collect, you can use the AWS Console to generate the configuration JSON.
Navigate to an EC2 instance and click Configure CloudWatch agent:
- Walk through the wizard and select the metrics you want
- On the final step, you'll see the generated JSON configuration
- Copy this JSON and use it in your CDK code
You can also refer to the CloudWatch Agent configuration documentation for all available options.