Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling Groups with .NET and AWS CDK: Automated Scaling for Your Applications
Learn how to upgrade your EC2 infrastructure from manual instance management to automated scaling using Auto Scaling Groups. We'll explore Launch Templates, integrate with CodeDeploy, and see how your deployments stay automated as your infrastructure scales.
Manually managing EC2 instances quickly becomes impractical as your application grows.
You need infrastructure that automatically responds to traffic changes, replaces unhealthy instances, and maintains application availability without manual intervention.
Auto Scaling Groups solve this problem by automatically launching and terminating EC2 instances based on demand. When combined with CodeDeploy and Application Load Balancers, you get a fully automated deployment pipeline that scales with your application.
In this post, we'll create an Auto Scaling Group that automatically manages EC2 instances and registers them with a Target Group behind a Load Balancer.
We'll also configure CodeDeploy to work seamlessly with the Auto Scaling Group, ensuring your .NET application deployments remain automated even as your infrastructure scales up or down.
Deploying a .NET Web API on Amazon EC2: A Step-by-Step Guide

Thanks to AWS for sponsoring this article in my EC2 Series.
Quick Recap: The Current Setup
Before we dive into Auto Scaling Groups, let's quickly review what we have in place.
Our application is a .NET Web API that runs as a systemd service on EC2 instances. We've set up:
- Two EC2 instances created manually via AWS CDK
- A Target Group for load balancing
- A Load Balancer distributing traffic across instances
- CodeDeploy configured to deploy our application to both instances
- GitHub Actions workflow to automate deployments
Step-by-Step: Setting Up GitHub Actions to Build and Deploy .NET to EC2

The problem? Those two EC2 instances are created and added to the Target Group manually in our CDK code. If an instance goes down or we need to scale up, we have to update our infrastructure code and redeploy.
Let's fix that by introducing Auto Scaling Groups.
What is an Auto Scaling Group?
An Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling Group contains a collection of EC2 instances that are treated as a logical grouping for the purposes of automatic scaling and management.
The key benefit is that it helps you ensure you have the correct number of Amazon EC2 instances available to handle the load of your application.
You can specify:
- Minimum capacity: The minimum number of instances to keep running
- Maximum capacity: The maximum number of instances allowed
- Desired capacity: The target number of instances you want running
Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling automatically maintains the desired capacity by launching new instances when they fail, distributing them across Availability Zones, integrating with load balancers, and performing health checks to replace unhealthy instances.
For more details, check out the AWS Auto Scaling documentation.
Understanding Launch Templates
Before we create an Auto Scaling Group, we need to understand Launch Templates.
A Launch Template is a reusable blueprint that contains all the settings needed to create an instance—instance type, AMI, security groups, key pairs, and IAM roles.
When you use an Auto Scaling Group, it needs to know how to create new instances automatically. That's where Launch Templates come in—they provide all the necessary parameters so AWS can spin up instances without manual intervention.
You can create multiple versions of a Launch Template and reference specific versions in your Auto Scaling Group configuration.
For more information, see the AWS Launch Templates documentation.
Updating CDK to Use Auto Scaling Group
Let's update our AWS CDK stack to replace manual instance creation with an Auto Scaling Group.
Previously, our CDK code looked something like this:
// Old approach - manually creating instancesvar instance1 = new Instance_(this, "Instance1", new InstanceProps{InstanceType = InstanceType.Of(InstanceClass.BURSTABLE3, InstanceSize.MICRO),MachineImage = MachineImage.LatestAmazonLinux2023(),Vpc = vpc,SecurityGroup = securityGroup,Role = role,KeyPair = keyPair});var instance2 = new Instance_(this, "Instance2", new InstanceProps{...});// Manually adding to target grouptargetGroup.AddTarget(new InstanceIdTarget(instance1.InstanceId));targetGroup.AddTarget(new InstanceIdTarget(instance2.InstanceId));
Now let's replace this with a Launch Template and Auto Scaling Group:
// Create Launch Templatevar launchTemplate = new LaunchTemplate(this, "WebApiLaunchTemplate", new LaunchTemplateProps{LaunchTemplateName = "WebApiLaunchTemplate",InstanceType = InstanceType.Of(InstanceClass.BURSTABLE3, InstanceSize.MICRO),MachineImage = MachineImage.LatestAmazonLinux2023(),SecurityGroup = securityGroup,KeyPair = keyPair,Role = role});// Create Auto Scaling Groupvar autoScalingGroup = new AutoScalingGroup(this, "WebApiAutoScalingGroup", new AutoScalingGroupProps{Vpc = vpc,LaunchTemplate = launchTemplate,MinCapacity = 1,MaxCapacity = 4,DesiredCapacity = 2});// Attach to Target GroupautoScalingGroup.AttachToApplicationTargetGroup(targetGroup);
The key changes:
- Launch Template: Contains all the instance configuration that was previously defined for each instance
- Auto Scaling Group: References the Launch Template and specifies capacity settings
- Target Group Integration: Uses
AttachToApplicationTargetGroup()instead of manually adding instances
The Auto Scaling Group will now automatically create 2 instances, maintain between 1 and 4 instances, register new instances with the Target Group, and replace unhealthy instances.
Deploying the Changes
Let's deploy these changes to AWS by running cdk deploy. The CDK will show you a preview of the changes—review them and confirm the deployment.
Once the deployment completes, navigate to EC2 → Auto Scaling Groups in the AWS Console to see your new Auto Scaling Group in action. You'll see the group details including name, ARN, and creation time. The instance management section shows 2 currently running instances, and the capacity is set to Min (1), Max (4), Desired (2). The launch template being used to create instances is also displayed.
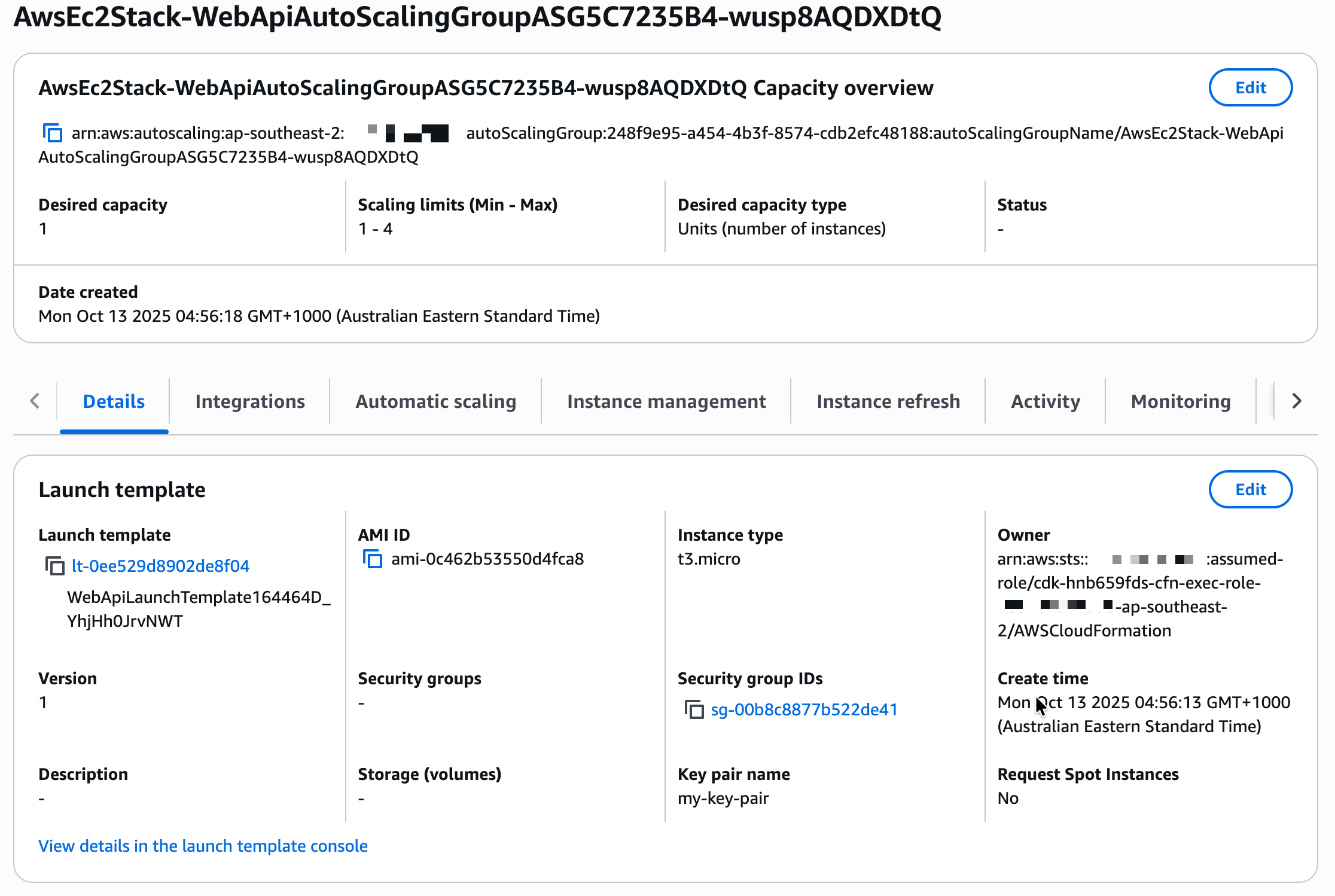
Click on the Auto Scaling Group to view more details. Under the Instance management tab, you'll see the two EC2 instances that were automatically created and registered.
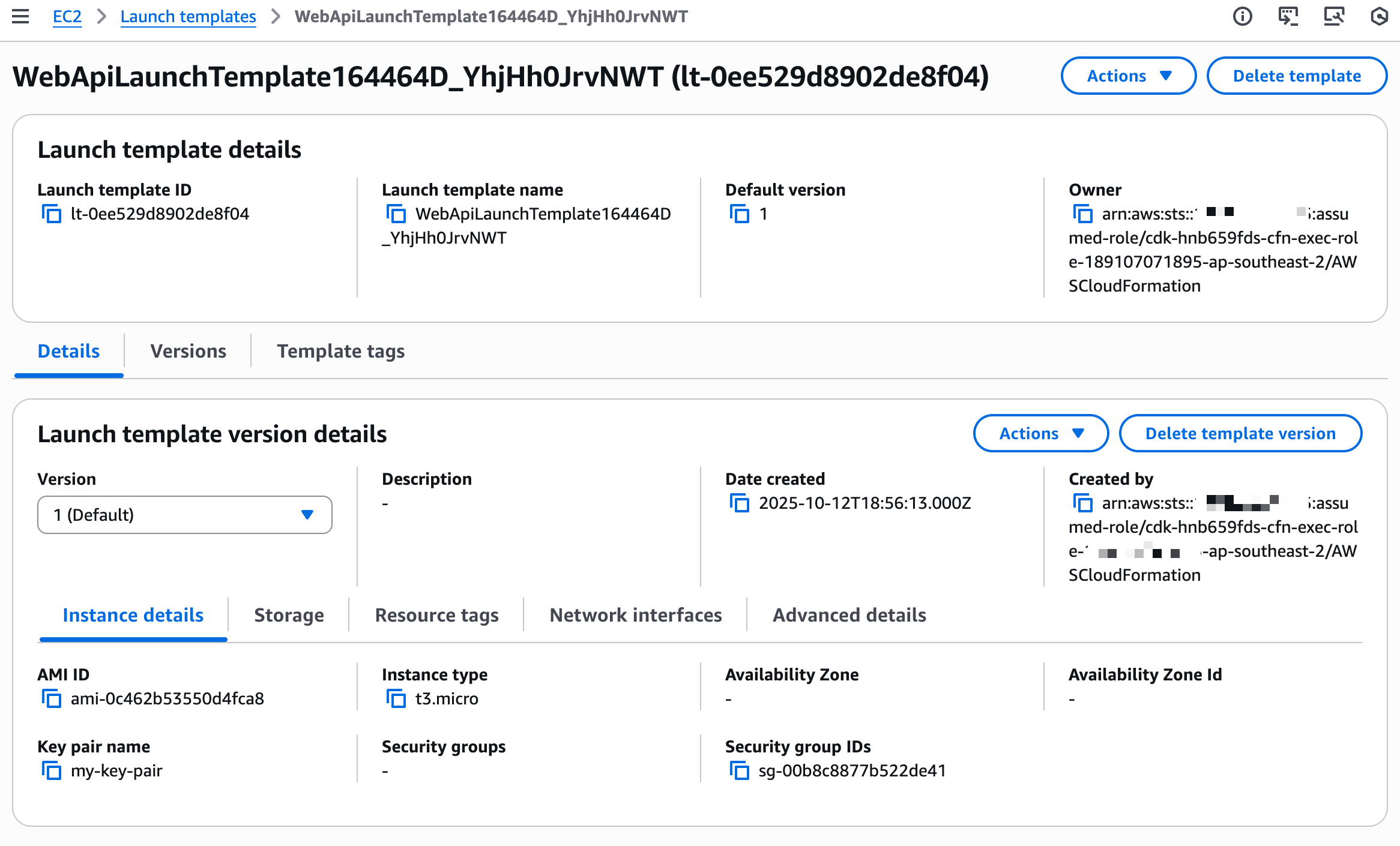
You can also navigate to EC2 → Launch Templates to see the template configuration. Click on your Launch Template to view the instance type (t3.micro), AMI (Amazon Linux 2023), security groups, IAM instance profile, and key pair. You can also view version information and create new versions if needed.
Integrating CodeDeploy with Auto Scaling Group
Now that we have an Auto Scaling Group, we need to update our CodeDeploy deployment group to target it instead of individual instances.
Deploying .NET Applications to EC2 Using AWS CodeDeploy

Navigate to CodeDeploy → Applications in the AWS Console. Select your application and click on the deployment group.
Click Edit to modify the deployment group configuration.
Previously, we targeted instances using tags. Now switch to targeting the Auto Scaling Group by removing the EC2 instances section, selecting Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling groups, choosing your Auto Scaling Group from the dropdown, and saving changes.
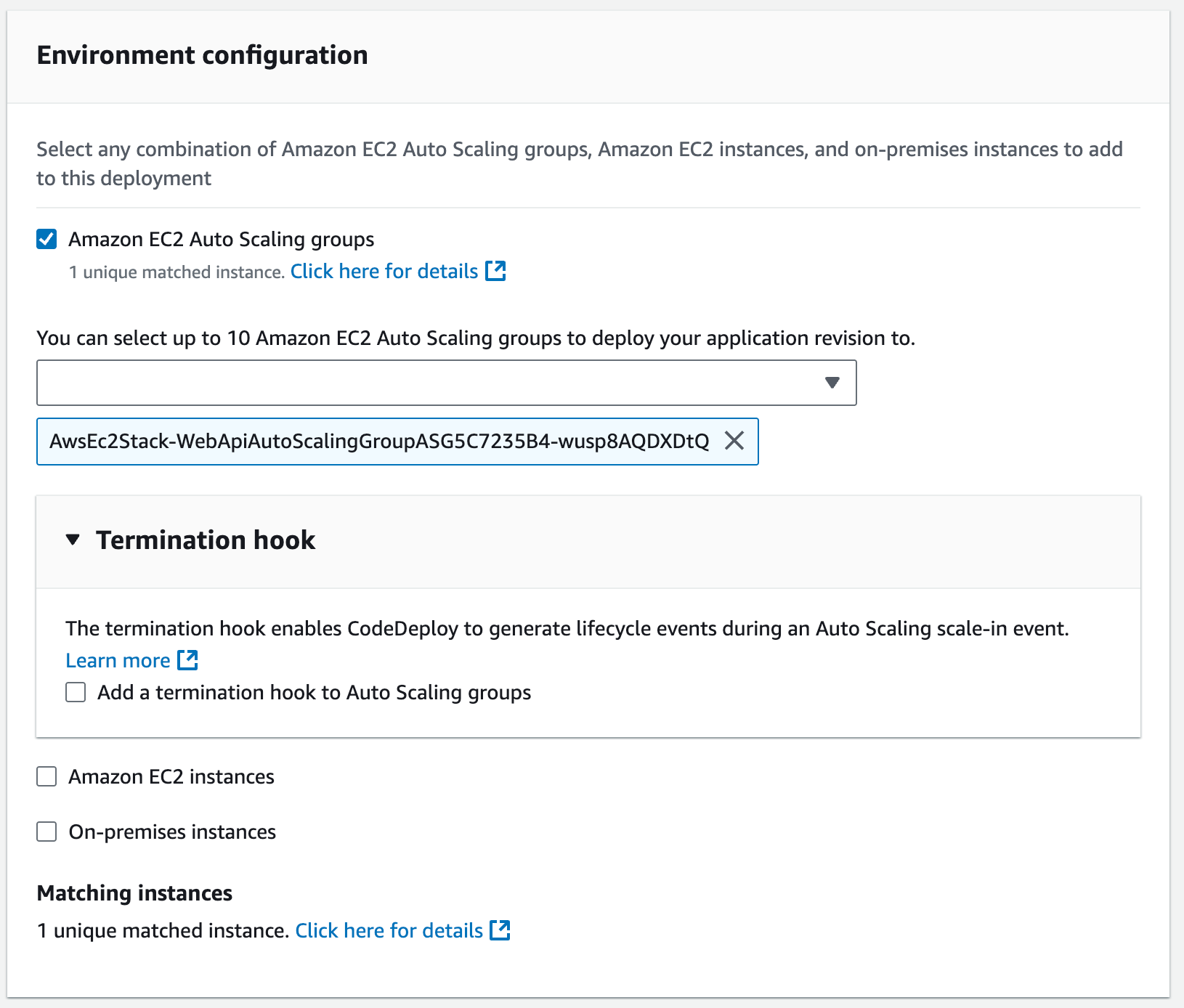
Now whenever the Auto Scaling Group creates a new instance, CodeDeploy will automatically deploy the latest application version to it.
Scaling Up: Adding More Instances
One of the key benefits of Auto Scaling Groups is the ability to easily scale your capacity.
Let's add a third instance to our Auto Scaling Group:
- Navigate to your Auto Scaling Group in the AWS Console
- Click Edit next to Group details
- Change Desired capacity from 2 to 3
- Click Update
The Auto Scaling Group immediately starts creating a new EC2 instance using the Launch Template. You can watch the progress under Instance management → Activity.
The new instance will show a lifecycle state of Pending while it's being created. Once it transitions to InService, CodeDeploy automatically triggers a new deployment to this instance.
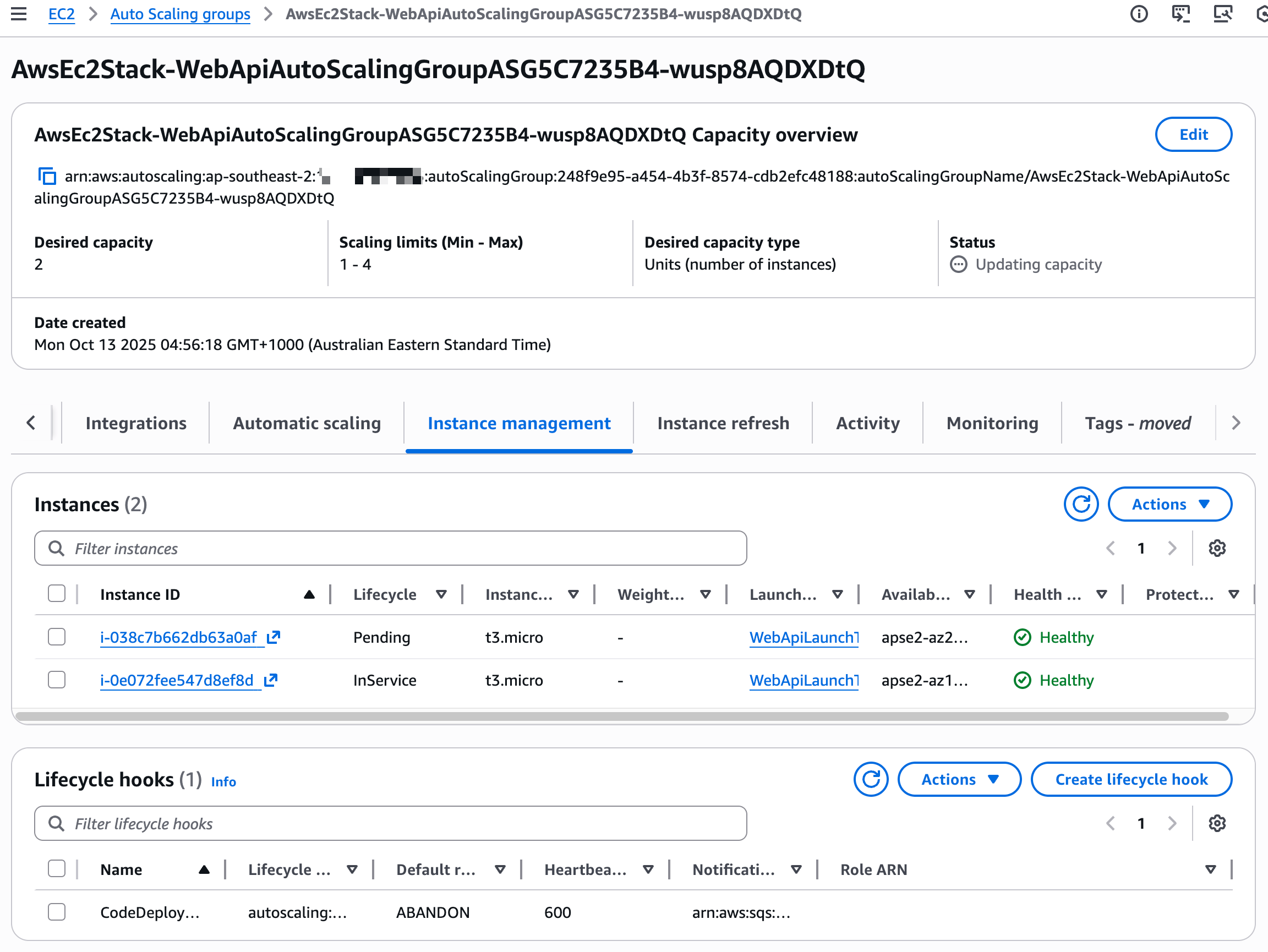
Navigate to CodeDeploy to see the automatic deployment in progress. It deploys the latest successful deployment to the new instance, ensuring consistency across your fleet.
Handling Instance Failures
Auto Scaling Groups also handle instance failures automatically.
Let's simulate a failure by terminating one of the instances:
- Navigate to EC2 → Instances
- Select one of your instances in the Auto Scaling Group
- Click Instance state → Terminate instance
- Confirm the termination
The Auto Scaling Group performs periodic health checks on instances. Once it detects the terminated instance is unhealthy, it:
- Marks the instance as Unhealthy
- Removes it from the Auto Scaling Group
- Launches a new instance to maintain the desired capacity
You can watch this happen in real-time under the Activity tab of your Auto Scaling Group.
Once the new instance is InService, CodeDeploy automatically deploys your application to it, ensuring zero manual intervention.
How Auto Scaling and CodeDeploy Work Together
The integration between Auto Scaling Groups and CodeDeploy is powered by activity triggers.
When you configure CodeDeploy to use an Auto Scaling Group as its deployment target, CodeDeploy automatically sets up triggers that respond to scaling events.
Whenever the Auto Scaling Group:
- Launches a new instance
- Replaces an unhealthy instance
- Scales up in response to demand
CodeDeploy receives a notification and automatically triggers a deployment using the most recent successful deployment for that application.
This ensures that all instances in your Auto Scaling Group are always running the same version of your application, regardless of when they were created.